Comparison of Two-Stroke and Four-Stroke Diesel Generator
On this page
Diesel generators serve as a critical emergency and backup power source, playing an indispensable role across various fields. From industrial facilities to residential communities, the application of diesel generators is extensive, ensuring continuous power support in the event of a main power outage. Based on the working cycle of diesel engines, diesel generators are primarily divided into two-stroke and four-stroke diesel generators. They each have distinct advantages and disadvantages in terms of design, performance, and application scenarios. This article will delve into these two types of diesel generators, analyze their pros and cons, and help users make wiser decisions when choosing.
Among the types of diesel generators, two-stroke diesel generators have garnered attention due to their unique design and functionality. Understanding the working mechanism and advantages of this type of generator is helpful in better grasping its applicable scenarios and potential limitations.
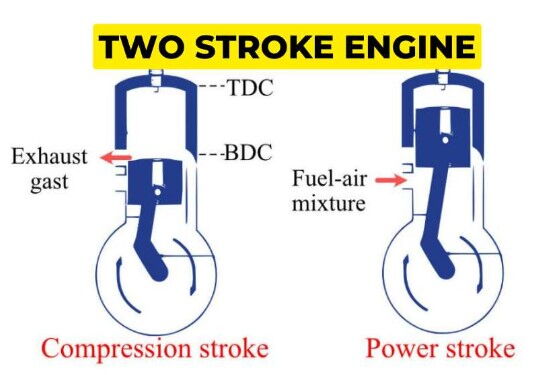
The core of a two-stroke diesel generator is the two-stroke diesel engine, which completes the entire process of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust within a single working cycle with only two strokes of the piston. Since it does not require a complex intake and exhaust valve system, the structural design of the two-stroke diesel generator is relatively simple, with fewer parts and a lighter weight.
Compact structure, easy to move: Due to its simple design, two-stroke diesel generators are usually smaller in size and lighter in weight, making them very suitable for applications that require portability and mobility. For example, in outdoor construction, emergency rescue, and small outdoor activities, two-stroke diesel generators are favored for their portability and ease of operation.
High power output: Thanks to the completion of two strokes by each piston within a single working cycle, two-stroke diesel generators can provide a higher power output in a shorter period of time. This makes them excellent for certain scenarios that require high power and rapid response, such as marine generators and emergency power for some industrial equipment.
Low fuel efficiency, high operating costs: The intake and exhaust processes of two-stroke diesel generators occur simultaneously, leading to incomplete combustion and thus lower fuel efficiency. This means that during long-term operation, two-stroke diesel generators consume more fuel, resulting in relatively high operating costs.
High emissions, not environmentally friendly: Due to the incomplete combustion, the exhaust gases of two-stroke diesel generators contain more unburned fuel and harmful gases, causing significant environmental pollution. This emission characteristic limits the use of two-stroke diesel generators in areas with strict environmental regulations.
Compared to two-stroke diesel generators, four-stroke diesel generators have a more complex design but also offer higher combustion efficiency and lower emissions. A thorough exploration of the characteristics of four-stroke diesel generators can help users make wiser choices when they require long-term stable power supply.
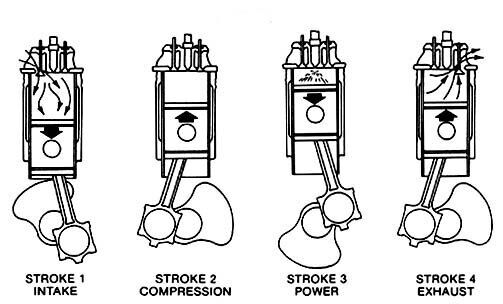
Four-stroke diesel generators use a four-stroke diesel engine, with a working cycle that includes four stages: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, each completed by four strokes of the piston. Since the intake and exhaust processes are controlled by separate valves, four-stroke diesel generators have higher combustion efficiency and cleaner emissions.
High fuel efficiency, cost-effective: The design of four-stroke diesel generators allows for more complete intake and exhaust processes, significantly improving combustion efficiency. This not only reduces fuel consumption and lowers operating costs but also extends the continuous working time of the diesel generator, making it very suitable for scenarios that require long-term stable power supply, such as data centers, hospitals, and factories.
Superior environmental performance, good emission control: Thanks to the complete combustion process, four-stroke diesel generators emit less exhaust gas and can meet stricter environmental standards. This makes four-stroke diesel generators widely used in urban power supply, residential areas, and industrial fields with high environmental requirements.
Smooth power output, low vibration and noise: The power output of four-stroke diesel generators is more balanced, reducing equipment vibration and noise caused by power fluctuations. This smoothness makes four-stroke diesel generators very suitable for scenarios with strict requirements for vibration and noise, such as high-end shopping malls, hospitals, and residential areas.
Complex structure, high maintenance difficulty: The design of four-stroke diesel generators is more complex, especially their intake and exhaust valve systems require precise adjustment, which increases the difficulty of maintenance and repair. In long-term use, four-stroke diesel generators may require more frequent maintenance, especially under high-load operation.
Large size, heavy weight: Due to the complex internal structure of four-stroke diesel generators, their overall volume and weight are larger, making them unsuitable for applications with limited space or frequent movement. For fixed backup power systems, such as factories and commercial buildings, the size and weight of four-stroke diesel generators are usually not a problem, but they are not ideal for portable applications.
After understanding the characteristics of two-stroke and four-stroke diesel generators, choosing the appropriate type of generator is particularly important. By combining actual application needs and clarifying the best use scenarios for different generators, the efficiency and reliability of the power supply system can be effectively improved.
Due to their high power output and compact design, two-stroke diesel generators are very suitable for scenarios that require lightweight and high mobility. For example, in outdoor construction, wilderness exploration, emergency rescue, and temporary power supply needs, the portability and ease of operation of two-stroke diesel generators make them an ideal choice. However, in scenarios that require long-term power supply and have strict emission requirements, the use of two-stroke diesel generators may be limited.
With their high fuel efficiency, low emissions, and smooth power output, four-stroke diesel generators are widely used in fixed installation scenarios that require long-term stable power supply. For example, in hospitals, data centers, industrial plants, and high-end residences, where there are high demands for power reliability, environmental protection, and low noise, four-stroke diesel generators become the first choice. In addition, the lower operating costs and longer service life of four-stroke diesel generators make them more economical in long-term operation.
Two-stroke and four-stroke diesel generators each have their pros and cons, suitable for different application needs. Two-stroke diesel generators, with their high power output and portable design, are suitable for short-term, temporary, and highly mobile power supply needs, while four-stroke diesel generators, with their high fuel efficiency, environmental performance, and stability, are widely used in long-term, fixed power supply scenarios. When choosing a diesel generator, users should consider the specific usage scenario, power supply needs, and environmental requirements, and comprehensively consider power output, fuel consumption, emission control, and maintenance convenience to choose the most suitable type of diesel generator, ensuring the reliability and cost-effectiveness of the equipment.
